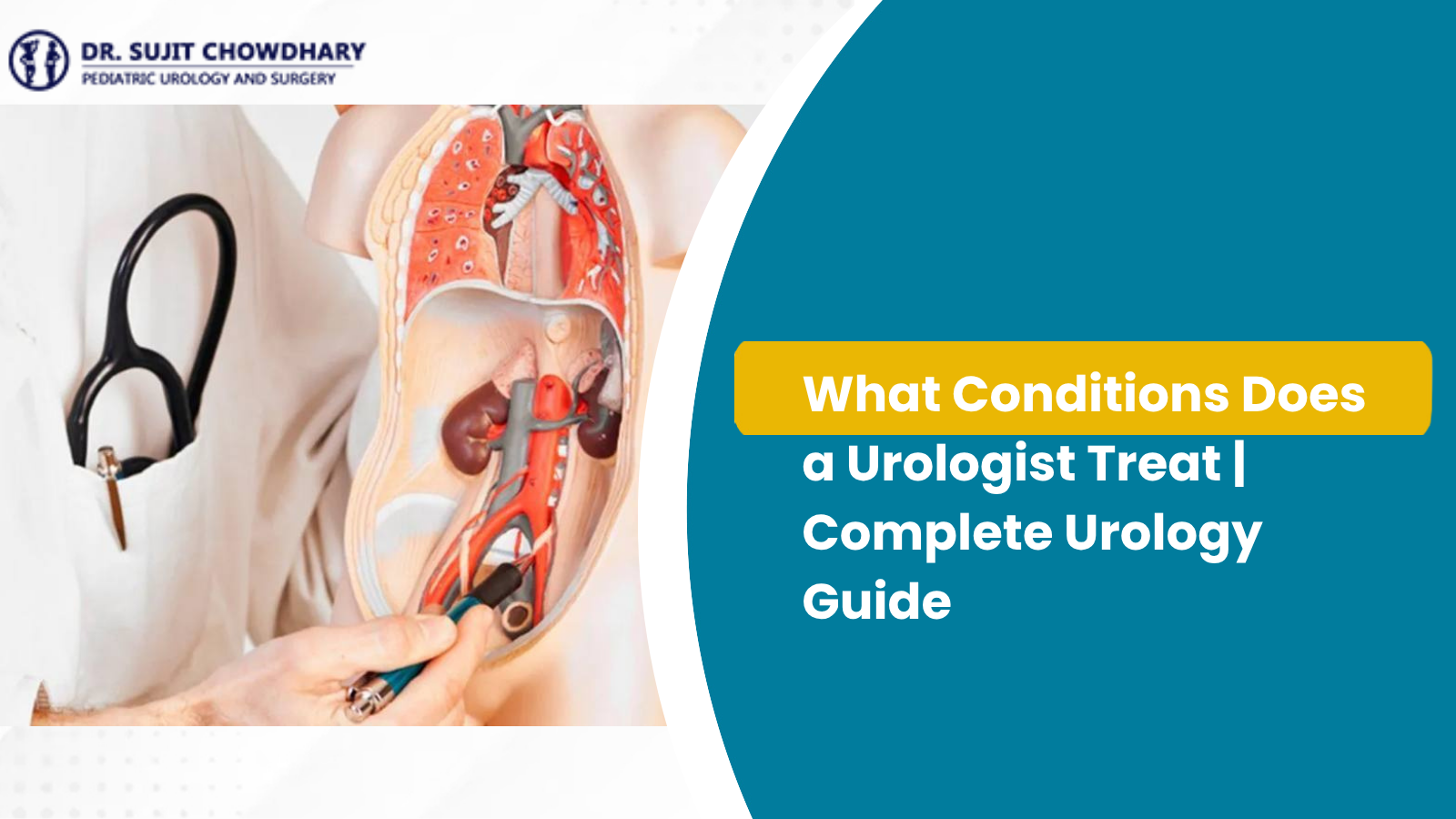
What Conditions Does a Urologist Treat? That’s an excellent question, and the answer is far more comprehensive than most people realize. A urologist is a physician and surgeon who specializes in the disorders of the male and female urinary tract, as well as the male reproductive organs. They are the experts who manage the structural, functional, and anatomical problems from your kidneys all the way out.
Unlike a nephrologist (who manages kidney function medically), a urologist provides the specialized surgical and medical management for diseases that physically impact the entire genitourinary system. This guide will walk you through the vast scope of urology, highlighting the key conditions treated across all ages and genders.
The Urologist’s Domain: An Overview
Urology, often referred to as “Genitourinary Surgery,” covers organs that are critical for filtering waste and for reproduction. When you ask What Conditions Does a Urologist Treat, you are essentially asking about the health of this entire, interconnected system:
- For all genders: The kidneys (for masses, stones, and obstructions), the ureters (tubes from kidney to bladder), the bladder, and the urethra (the tube for urine exit).
- For males: The prostate gland, testicles, penis, epididymis, and vas deferens (the entire reproductive tract).
- For females: Urologists treat female urinary issues, including urinary incontinence, prolapse, and recurrent infections, often in collaboration with gynecologists.
The core of a urologist’s expertise is the ability to offer a full spectrum of care, from simple medical advice and medication to complex robotic or open surgery.
Urologic Oncology (Cancers)
A major part of What Conditions Does a Urologist Treat involves the diagnosis and surgical management of cancers in the genitourinary system. Early detection and expert surgical removal are often key to cure.
A. Cancers of the Urinary System
- Kidney Cancer: Urologists perform partial or radical nephrectomy (removing part or all of the kidney), often using minimally invasive techniques like robotic or laparoscopic surgery, to remove tumors.
- Bladder Cancer: The urologist diagnoses this via cystoscopy (a camera placed into the bladder) and performs transurethral resection of the bladder tumor (TURBT). For advanced cases, they perform a cystectomy (bladder removal) and reconstruct a new urinary pathway (urinary diversion).
- Adrenal Gland Tumors: While not strictly part of the urinary tract, the adrenal glands sit atop the kidneys, and tumors here are often surgically removed by urologists via adrenalectomy.
B. Cancers of the Male Reproductive System
- Prostate Cancer: This is the most common non-skin cancer in men. Urologists manage the entire spectrum, from surveillance for low-risk disease to definitive treatment with radical prostatectomy (robotic, laparoscopic, or open) or radiation/hormone therapy.
- Testicular Cancer: Although less common, it is the most common solid tumor in young men. The urologist performs the diagnostic and therapeutic surgery (orchiectomy) and coordinates follow-up care.
- Penile Cancer: Rare, but managed by urologists, often requiring specialized surgical reconstruction.
Male-Specific Conditions
When discussing What Conditions Does a Urologist Treat, the distinction between male and female issues is important, especially concerning the prostate and reproductive health.
A. Prostate Disease
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH): This is the non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate, which causes bothersome lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) like frequent urination, weak stream, and incomplete emptying. Urologists offer a progression of treatments: medications, and minimally invasive procedures like UroLift, Rezum, or surgical procedures like Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) or Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate (HoLEP).
- Prostatitis: Inflammation or infection of the prostate, which can cause significant pain and discomfort.
B. Male Sexual and Reproductive Health (Andrology)
- Erectile Dysfunction (ED): The urologist diagnoses the cause (vascular, neurological, hormonal, or psychological) and offers treatments ranging from oral medications (like PDE5 inhibitors) to penile injections, vacuum erection devices, and, when necessary, penile implant surgery.
- Male Infertility: Urologists evaluate low sperm count or poor sperm quality, often performing corrective procedures like varicocelectomy (repair of an enlarged vein in the scrotum) or surgical sperm retrieval.
- Peyronie’s Disease: A condition causing abnormal curvature of the penis due to scar tissue (plaque), managed with injections or surgical correction.
- Testicular/Scrotal Issues: Including hydroceles (fluid around the testicle), varicoceles, and managing acute pain like testicular torsion.
Female-Specific Conditions (Female Urology)
The field of Female Urology focuses on issues of the female urinary tract and pelvic floor, a key part of What Conditions Does a Urologist Treat.
- Urinary Incontinence: This is the involuntary leakage of urine. Urologists identify the type (Stress, Urge, or Mixed) and treat it with behavioral therapy, pelvic floor exercises (Kegels), medications, or surgical procedures like mid-urethral slings.
- Overactive Bladder (OAB): Characterized by sudden, strong urges to urinate (urgency), often leading to incontinence. Treatments include lifestyle changes, medications, and advanced therapies like Botox injections into the bladder muscle or sacral neuromodulation (nerve stimulation).
- Pelvic Organ Prolapse: When the bladder or other pelvic organs descend into the vagina. Urologists (or Urogynecologists, a related specialty) perform reconstructive surgery to restore pelvic support.
- Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome (IC/BPS): A chronic condition causing painful bladder and pelvic discomfort.
Urinary Tract Calculi (Stones) and Infections
Kidney stones and recurrent infections are among the most common reasons people seek a urologist.
A. Kidney Stones and Bladder Stones
Kidney stones are hard masses made of crystallized minerals and salts that can cause excruciating pain when they block the ureter. Urologists are experts in the surgical removal and management of these stones.
- Lithotripsy (ESWL): Using shock waves from outside the body to break stones into small pieces.
- Ureteroscopy (URS): Placing a small scope through the urethra and bladder into the ureter to visualize and laser the stone.
- Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL): A minimally invasive surgical procedure for very large kidney stones.
- Metabolic Evaluation: Urologists may also perform tests to determine the stone’s composition and advise on preventative measures (diet and medication).
B. Infections and Inflammations
- Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): While a primary care doctor treats simple UTIs, a urologist is crucial for investigating the underlying cause of repeated infections, especially in men and children, or when there is blood in the urine (hematuria).
- Pyelonephritis: Severe kidney infections, which may require urologic intervention if an obstruction (like a stone) is present.
Pediatric Urology: Specialized Care for Children
The most highly specialized subfield within the answer to What Conditions Does a Urologist Treat is Pediatric Urology. This subspecialty focuses on the unique urinary and reproductive issues of infants, children, and adolescents. A specialist like a Pediatric Urologist in India is essential because children’s bodies are still developing, and conditions present differently than in adults.
The scope of a Pediatric Urologist in India includes:
- Congenital Anomalies: Birth defects like Hypospadias (abnormal urethral opening), Epispadias, and Bladder Exstrophy.
- Undescended Testicles (Cryptorchidism): A common condition requiring surgical correction (orchidopexy).
- Hydronephrosis: Swelling of the kidney due to blockage, often managed with surgery like a pyeloplasty.
- Vesicoureteral Reflux (VUR): The backflow of urine from the bladder to the kidneys, increasing the risk of kidney damage.
- Voiding Dysfunction: Complex issues with urination, including bedwetting (enuresis) and daytime incontinence that is resistant to standard care.
Expert specialists like Dr. Sujit Chowdhary, whose practice often encompasses the delicate nature of pediatric and reconstructive urology, provide critical surgical and medical care for these young patients. His focus on minimally invasive techniques for complex conditions is a hallmark of the advanced care available from a Pediatric Urologist in India.
Conclusion: Expertise You Can Trust
The question of What Conditions Does a Urologist Treat leads us through a vast and critical area of medicine. From managing the common nuisance of kidney stones to performing life-saving robotic surgery for prostate cancer, urologists cover a comprehensive range of health issues.
Whether you require delicate procedures for a child by a specialist like Доктор Суджит Чоудхари , whose expertise is often in Pediatric Urologist in India and reconstructive urology, or need advanced care for adult urological concerns, the right expertise is crucial. Understanding the breadth of this specialty empowers you to seek the right care for issues affecting your urinary tract and, for men, your reproductive health. Don’t hesitate to consult a specialist if you experience symptoms related to the conditions discussed above.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ):
1. What are the most common conditions treated by a urologist?
A urologist treats a wide range of conditions, including kidney stones, urinary tract infections (UTIs), bladder problems, prostate enlargement, erectile dysfunction, infertility, and cancers of the urinary or reproductive system.
2. Do urologists treat both men and women?
Yes, urologists treat both men and women. They manage urinary system disorders in both genders, while also handling male-specific conditions such as prostate disease, erectile dysfunction, and infertility.
3. What types of cancers do urologists treat?
Urologists treat cancers of the urinary and reproductive organs, including kidney, bladder, prostate, testicular, adrenal, and penile cancers. They perform diagnostic procedures and surgical treatments for these cancers.
4. Can a urologist help with urinary incontinence?
Yes. Urologists are experts in diagnosing and treating urinary incontinence in both men and women. Treatment options may include medication, pelvic floor exercises, or minimally invasive surgical procedures.
5. Do urologists treat kidney stones?
Absolutely. Kidney stones are one of the most common problems treated by urologists. Treatment options include lithotripsy (shock wave therapy), ureteroscopy (laser removal), and minimally invasive surgeries like PCNL.